CAS Protocol Overview¶
Introduction¶
The CAS protocol is a simple and powerful ticket-based protocol for single sign on. A complete protocol specification may be found CAS-Protocol-Specification.
It involves one or many clients and one server.
The CAS server is responsible for authenticating users and granting accesses to applications.
The CAS clients protect the CAS applications and retrieve the identity of the granted users from the CAS server.
The key concepts are:
The TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket), stored in the CASTGC cookie, represents a SSO session for a user.
The ST (Service Ticket), transmitted as a GET parameter in urls, stands for the access granted by the CAS server to the CASified application for a specific user.
Specification versions¶
The current CAS protocol specification is 3.x. The actual protocol specification is available at CAS-Protocol-Specification. It’s mainly a capture of the most common enhancements built on top of the CAS protocol revision 2.0. Among all features, the most noticeable update between versions 2.0 and 3.0 is the ability to return the authentication/user attributes through the new /p3/serviceValidate response (in addition to the /serviceValidate endpoint, already existing for CAS 2.0 protocol).
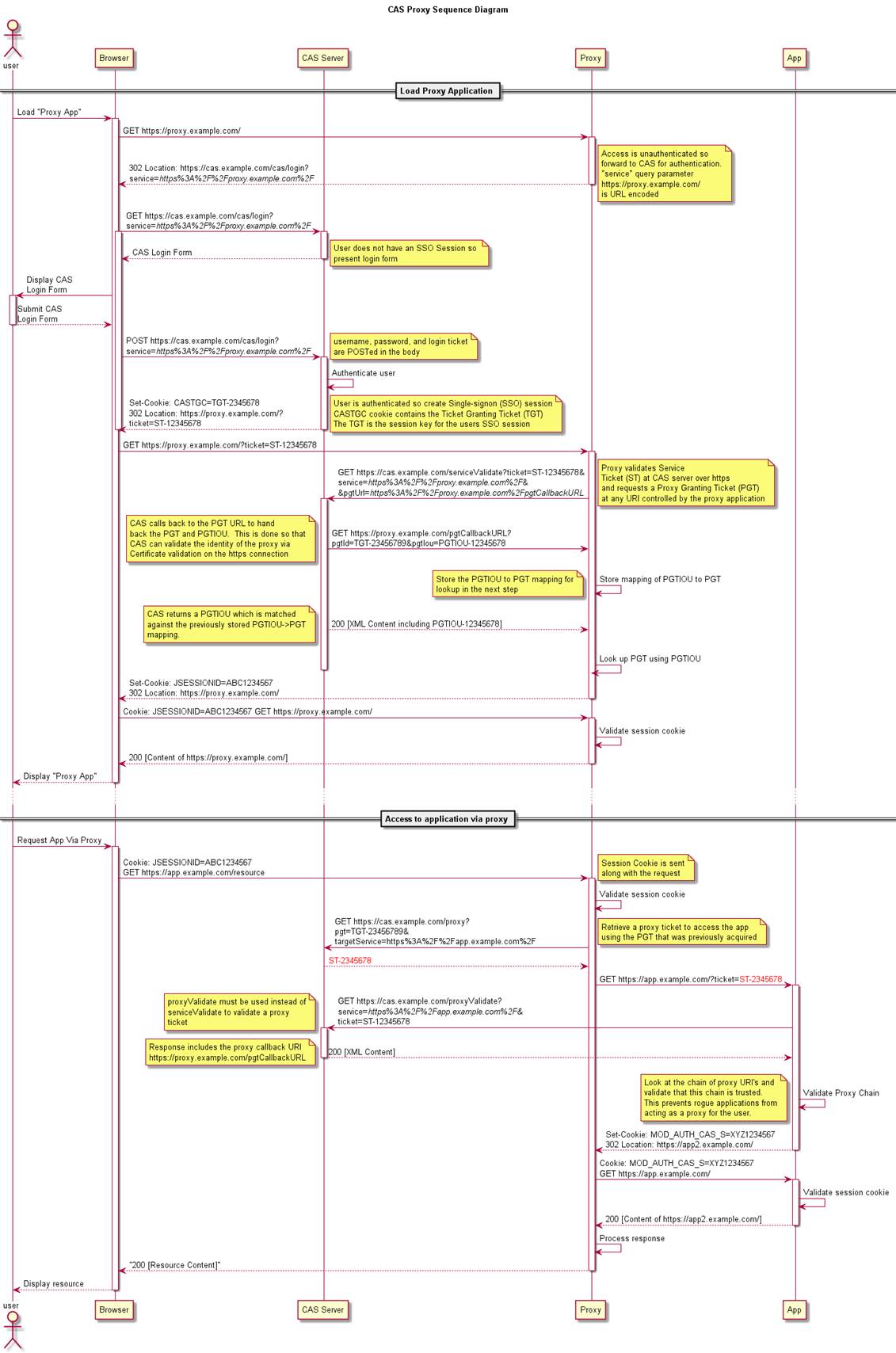
Web flow diagram¶
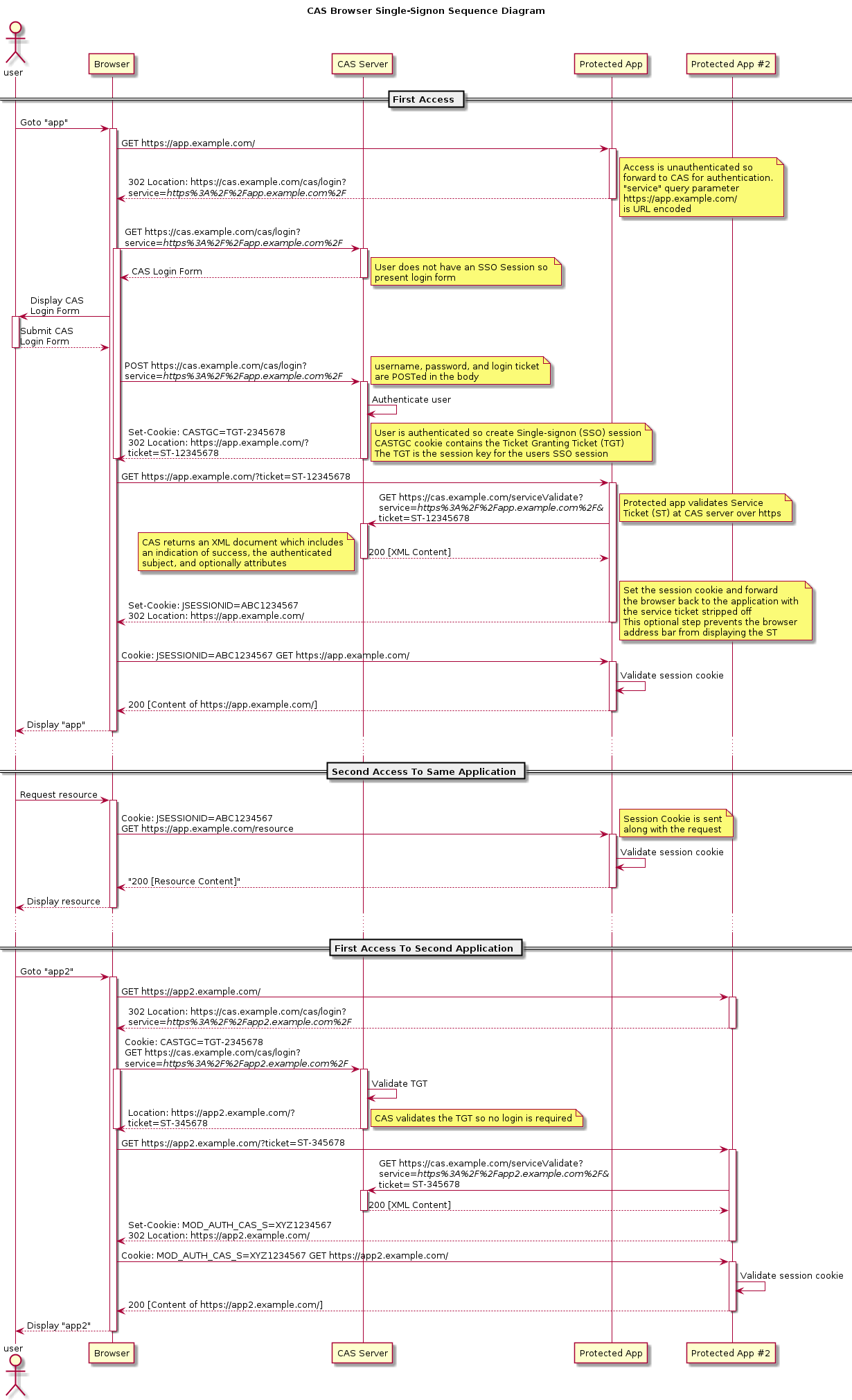
Proxy web flow diagram¶
One of the most powerful feature of the CAS protocol is the ability for a CAS service to act as a proxy for another CAS service, transmitting the user identity.